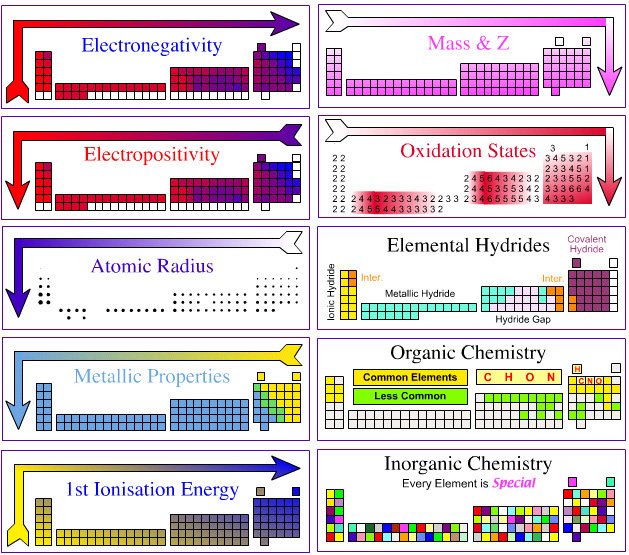
Today we leanred about fuctional groups. They are called hydrocarbon derivatives. It is because the carbon is bonded other than hydrogen. Each specific functional group gives rise to a family of organic compounds.
 Example incude: Halocarbons, alcohols, organic acids, aldehydes, ketones, ethers, esters, amilines, and amides.
Example incude: Halocarbons, alcohols, organic acids, aldehydes, ketones, ethers, esters, amilines, and amides.
1) Halides and Nitro Compound
-Halocarbons: R-X where X=F,Cl,Br,I
-A halocarbon is an organic compound with a halogen atom(F,Cl,Br,I) bonded to its structure.
-Nitro compound is same as Halides except only No2 is attached to the Carbon


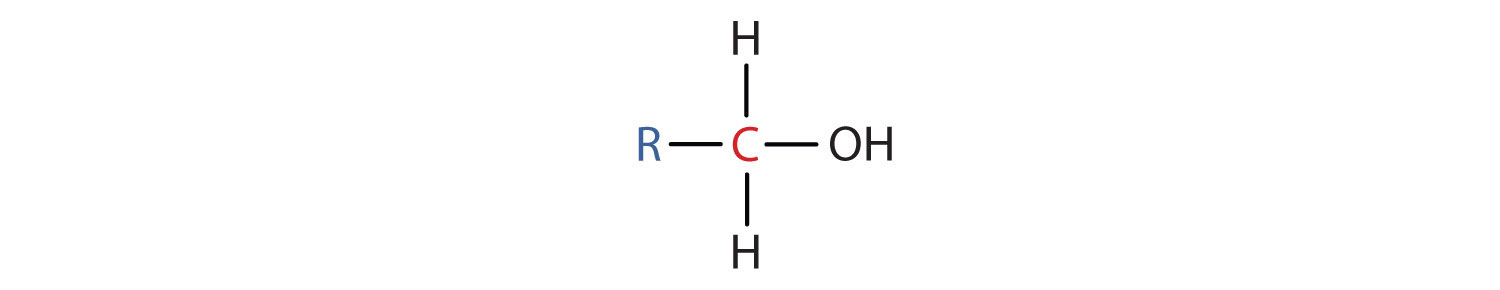
Alcohols
- Is formed from a hydrocarbon that is convalently bonded to a hydroxyl group.
-expressed as R-OH where R represents a hydrocarbon chain or ring and OH represents at least one hydroxly group consisting of an exygen atom and a hydrogen atom.
Naming alcohols
-find parent chain containing the hydroxy group(OH)
-change ending to ol
-OH gets lowest possible locant
-when more than one OH include Greek prefixes.
Eg: Two OH groups are labelled diol
Kentones
-Almost same as Alhydes
-The double bonded oxygen to the carbon chain is somewhere in the middle. Unlike Alhydes it is always in the beginning or end
-stucture is R-Co-R
Naming
-Add one for the ending
-locate the ketones with lowest subscripts in the chain
That concludes what we had lernt today. Now review again with these cool interesting videos!!!!!!!!
 Example incude: Halocarbons, alcohols, organic acids, aldehydes, ketones, ethers, esters, amilines, and amides.
Example incude: Halocarbons, alcohols, organic acids, aldehydes, ketones, ethers, esters, amilines, and amides. The main ones we will focus on are:
Halides & Nitro Compound
Halides & Nitro Compound
Alcohols
Aldehydes & Ketones
Aldehydes & Ketones
1) Halides and Nitro Compound
-Halocarbons: R-X where X=F,Cl,Br,I
-A halocarbon is an organic compound with a halogen atom(F,Cl,Br,I) bonded to its structure.
-Nitro compound is same as Halides except only No2 is attached to the Carbon


Alcohols
- Is formed from a hydrocarbon that is convalently bonded to a hydroxyl group.
-expressed as R-OH where R represents a hydrocarbon chain or ring and OH represents at least one hydroxly group consisting of an exygen atom and a hydrogen atom.
Naming alcohols
-find parent chain containing the hydroxy group(OH)
-change ending to ol
-OH gets lowest possible locant
-when more than one OH include Greek prefixes.
Eg: Two OH groups are labelled diol
 |
| Ethanol |
Aldehydes
-Gerneral formula is R-COH
-A Carbon in a chain is double bonded to an oxygen and single bonded to a hydrogen
Naming
-add al at the end
 |
| 2-methylbutanal |
-Almost same as Alhydes
-The double bonded oxygen to the carbon chain is somewhere in the middle. Unlike Alhydes it is always in the beginning or end
-stucture is R-Co-R
Naming
-Add one for the ending
-locate the ketones with lowest subscripts in the chain
| 3-methy-2-pentanone |